Medical records hold deep value for hospitals, insurance providers, and patients. Coding inside hospitals stands as the spine of this healthcare recordkeeping. Healthcare coding, or medical coding, makes sure that every piece of patient information stays arranged in a clear order. Medical coding acts as a form of communication. It speaks for treatment billing and record purposes.
Let us uncover the weight of coding in medical billing and how the process unfolds.

What is Coding in Medical Billing?
Medical coding is the act of turning healthcare actions into fixed and recognized codes. This record covers every step within a medical care journey. From diagnosis to medical services and tools used along the way. Medical coders shift these details into code form.
What does coding mean in a Hospital?
This coding in hospitals and healthcare settings later settles inside your medical records. It serves as the core for insurance claims billing setups and healthcare data systems.
Medical coding reshapes a patient’s medical details into a shared language that both healthcare systems and insurance companies can grasp with clarity.
Medical coding example:
→ When a patient is found to have diabetes. Writing the full explanation of the illness and related procedures takes extra time and effort. In place of that, medical coders mark a set code taken from standard coding books, such as ICD-10, also known as the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision.
This code tells everyone exactly what condition the patient has. This practice successfully avoids confusion and ensures accurate medical billing.
Why Medical Coding is Important?
Healthcare coding serves multiple crucial functions in healthcare:
→ Accurate Billing: Insurance firms depend on medical codes to handle claim processing. Without correct codes, healthcare centers might not receive proper payment for their services.
→ Data Standardization: Standardized codes make the exchange of patient details smoother between hospitals, clinics, and medical experts. Written details without medical codes will create confusion and cause many flaws.
→ Health Statistics and Research: Medical codes in healthcare help track disease trends. They play a strong role in tracking public health and guiding medical research.
→ Legal Compliance: Proper medical coding inside hospitals makes sure that healthcare providers stay aligned with national and state rules. It also helps them steer clear of fines and audits.
→ Quality Patient Care: Correct medical codes show a clear picture of a patient’s health state. This helps doctors choose better paths for treatment and care.
What are Key Medical Coding Systems?
Healthcare makes use of many coding systems. Each one carries its own task and reason for being. Below is a clear look at the main types.
1. ICD Codes (International Classification of Diseases)
The World Health Organization oversees ICD codes. They are practiced by countries all around the world. These codes outline disease symptoms and medical states.
The version applied in the United States under HIPAA includes:
ICD-10-PCS (Procedural Coding System): This system holds over seventy-five thousand alphanumeric codes. It is used to signify and detail surgical or procedural actions.
ICD-10-CM (Clinically Modified): This version holds around seventy thousand codes. It is used to portray illnesses or disease conditions faced by patients.
2. CPT® Codes (Current Procedural Terminology)
The American Medical Association maintains CPT codes. This collection includes more than eleven thousand codes. It is used to register and define medical services and procedures carried out by healthcare professionals.
3. HCPCS Codes (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System)
HCPCS codes handle medical services and items not found under CPT codes. They are used when a service or product needs its own unique identifier. These codes apply to areas like ambulance transport, prosthetic devices, and durable medical equipment. They hold major importance in Medicare and Medicaid billing.
4. MS-DRG and APC
MS-DRG (Medical Severity Diagnosis-Related Groups) and APC are federal-level coding systems designed to regulate hospital payments. They function in coordination with ICD, CPT, and HCPCS codes.
MS-DRG (Medical Severity Diagnosis-Related Groups): This system is mainly used for inpatient hospital billing. It groups patients according to defined clinical criteria. These criteria include the main diagnosis, related conditions, and procedures performed.. Patient sex and discharge status are also reviewed during classification.
Each group helps hospitals secure accurate and fair reimbursement for the care delivered. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services manage this system in collaboration with 3M Health Information Systems.
APC (Ambulatory Payment Categories): APCs are mainly used for outpatient hospital services. These include minor treatments and small surgical procedures. APC medical codes classify outpatient services into payment categories. This system helps hospitals manage billing for short or same-day care.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services oversee APCs. They do this under the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System.
How is Medical Coding Done?
Medical coding goes beyond number selection. It follows a set path for accuracy:
1. Reviewing Medical Records
Medical coders start by reading detailed medical records, which may include:
- Patient history
- Physician notes
- Lab results
- Surgical reports
2. Identifying Diagnoses and Procedures
Medical coding professionals receive training to recognize key diagnoses. They also identify procedures and services provided during care. They study the medical documentation with close attention. This helps them prevent errors and keep records precise.
3. Assigning Codes
Using medical coding manuals like ICD, CPT, or HCPCS, medical coders assign the correct codes for each diagnosis and procedure.
Accuracy holds great importance in this process. Incorrect coding can cause claim rejections or even trigger audits.
4. Quality Check and Submission
Medical coding is completely done by a certified medical coding specialist. After that, the medical records often undergo a quality check. After verification, the codes are submitted to insurance companies for claim processing.
Medical Coding and Medical Billing: How They Work Together?
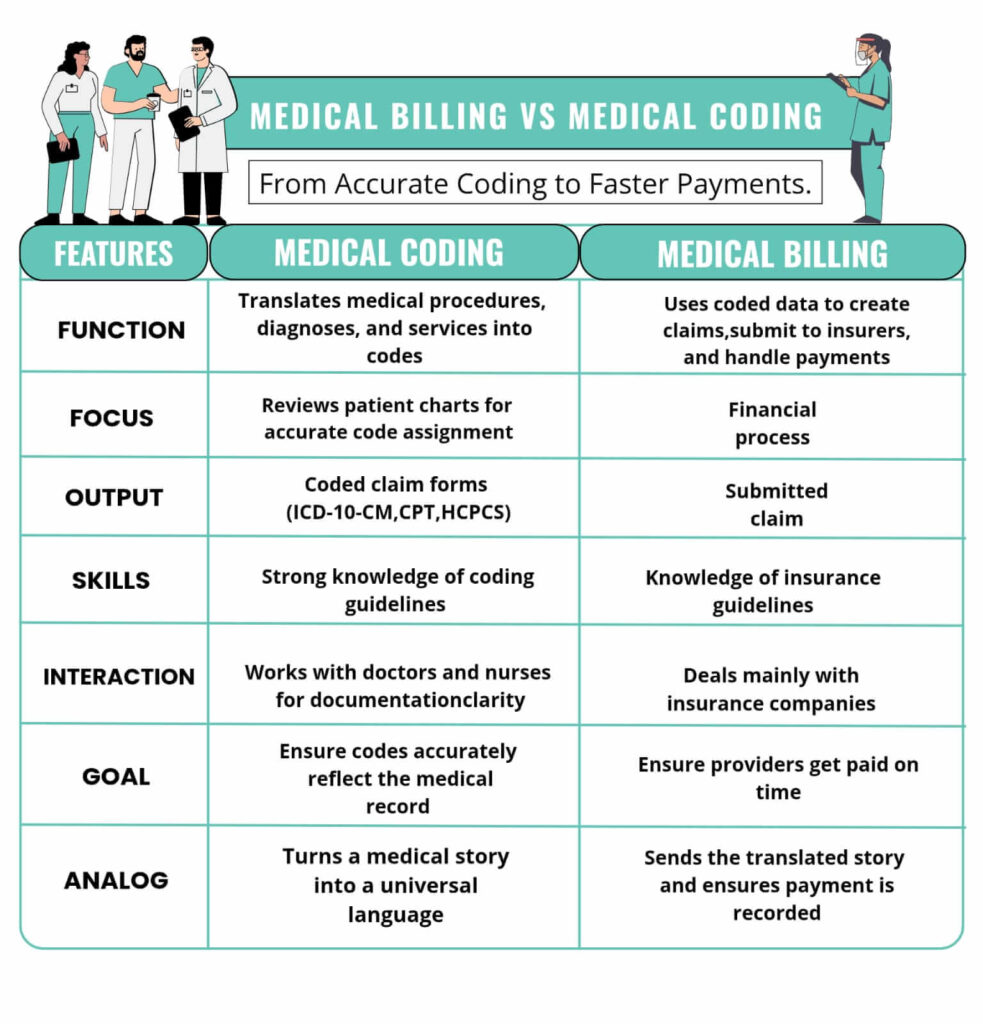
Medical coding and medical billing stand as core parts of Revenue Cycle Management. They move in close link, yet each holds its own task.
- Medical Coding: Deals with assigning codes that mirror diagnoses and procedures.
- Medical Billing: Uses those codes to issue bills and send claims to insurance bodies.
Without proper coding in hospitals and the entire healthcare system, the medical billing process would lose accuracy or fail entirely. At the same time, coders depend on complete and clear documentation from healthcare workers to mark codes with precision.
Challenges in Medical Coding
Medical coding is not without challenges:
- Complex Medical Terminology: Understanding medical jargon and procedures requires extensive training.
- Frequent Updates: ICD, CPT, and HCPCS codes are updated annually, requiring coders to stay current.
- Documentation Issues: Incomplete or unclear medical records can make coding difficult.
- Audits and Compliance: Errors can lead to claim denials, legal consequences, or financial losses.
Bottom Line
Medical coding stands as a vital piece of the healthcare structure. It ensures every patient’s condition and treatment are recorded with precision. It strengthens coordination between hospitals and insurance bodies. It also aids research, public health tracking, and legal compliance.
For new professionals, medical coding offers a stable and purposeful career. It allows steady growth and continuous learning. With proper training certification and strong focus, certified medical coders help shape quality care and smooth healthcare operations.



Comments are closed.